For those who have a passion for coffee and are adhering to a gluten-free diet, the question of whether coffee is safe to consume may arise. With the growing prevalence of gluten sensitivity and celiac disease, it is essential to be aware of which foods and drinks contain gluten and which ones do not. Therefore, the critical inquiry is: Is coffee gluten-free?
In this blog post, we will thoroughly explore the subject of whether coffee is gluten-free or not. We will delve into the intricacies of gluten, its impact on individuals with gluten sensitivity and celiac disease, and whether coffee encompasses gluten. Additionally, we will discuss the different ways in which coffee can come into contact with gluten and provide strategies to ensure that your coffee is harmless for you to ingest.
So, if you’re an enthusiast of coffee with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease, or merely inquisitive about the topic, continue reading to learn everything you must know regarding the relationship between coffee and gluten.
Grasping Gluten and Celiac Disease
Gluten is a protein that exists in grains such as wheat, barley, and rye. While the majority of people can consume gluten without any issues, those who have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity can encounter adverse reactions to even minor amounts of gluten.

Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder whereby the consumption of gluten instigates an immune response that harms the small intestine. This damage can result in a variety of symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and inadequate absorption of nutrients. If left untreated, celiac disease can lead to long-term health complications over time.
On the other hand, gluten sensitivity is a condition whereby an individual experiences similar symptoms to celiac disease, but without the immune response and damage to the small intestine. The exact cause of gluten sensitivity remains unknown, but numerous individuals report feeling better when they refrain from consuming gluten.
The Enigmatic Nature of Gluten
The multifaceted protein known as gluten is composed of two primary constituents: glutenin and gliadin. This protein can be found in various grains, such as wheat, barley, and rye. Gluten is renowned for conferring elasticity and chewiness to bread, which is why it is a prevalent ingredient in several baked goods.
Despite gluten not being innately harmful, it can induce undesirable reactions in individuals who suffer from celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
Gluten’s Origins and Manifestations
As previously mentioned, gluten is present in multiple grains, including but not limited to:
- Wheat
- Barley
- Rye
- Spelt
- Kamut
- Triticale (a composite of wheat and rye)
Furthermore, gluten can be detected in several products made from these grains, such as:
- Bread
- Pasta
- Cereal
- Baked goods (cakes, cookies, etc.)
- Beer
- Sauces and dressings
It is imperative to recognize that various foods that do not overtly contain gluten as an ingredient may still come into contact with gluten during processing. As such, it is necessary to be cautious when scrutinizing labels and selecting items.
Gluten’s Effects on the Body
Consuming gluten is known to prompt an immune reaction in individuals who have celiac disease, leading to intestinal harm and potential long-term complications. Meanwhile, gluten sensitivity can cause unwanted effects, although the exact biological mechanism remains incompletely comprehended.
Common symptoms of gluten sensitivity and celiac disease are as follows:
- Bloating
- Abdominal discomfort
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Skin rashes
- Anemia
- Malabsorption of nutrients
Individuals who suspect that they might have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity should seek the guidance of a healthcare professional to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of the condition.
What is Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is a multifaceted autoimmune disorder that arises when gluten consumption prompts an immune response that causes damage to the small intestine, resulting in a variety of symptoms that may include bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and malabsorption of nutrients. If left untreated, this condition may lead to significant health complications.
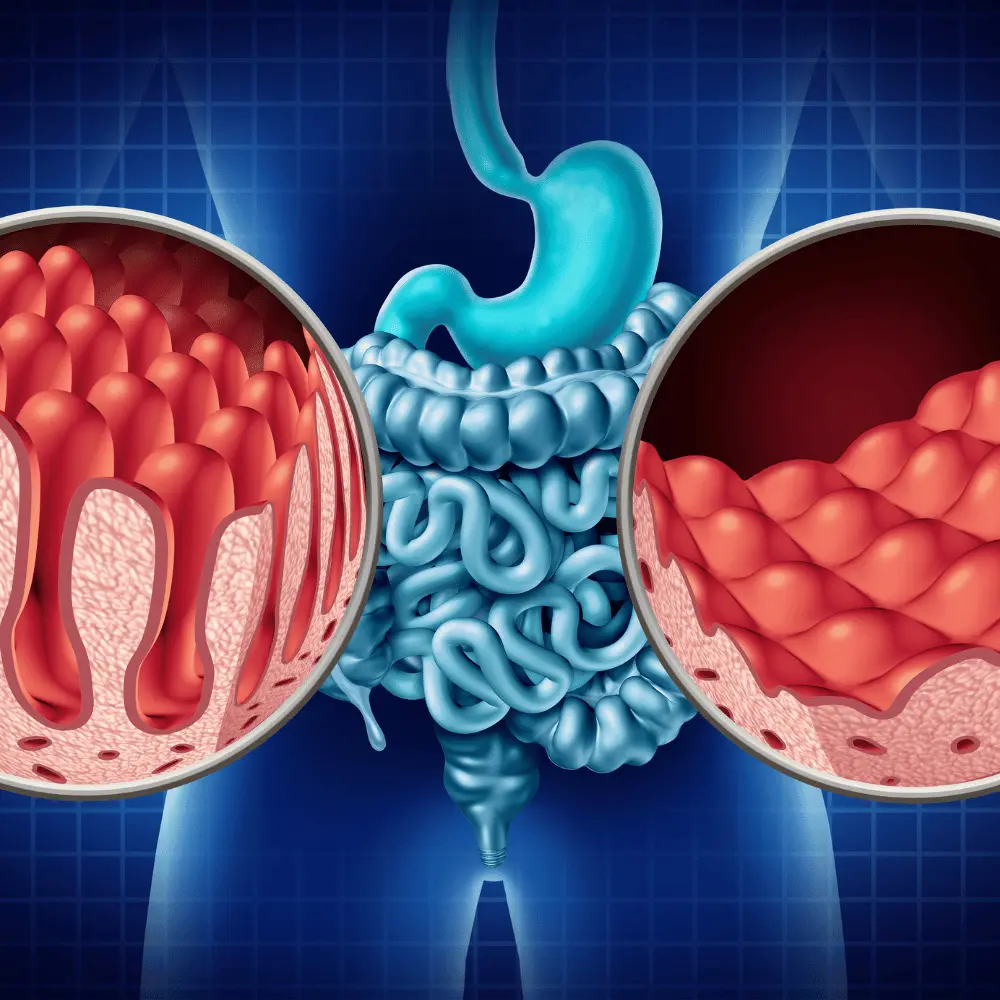
Globally, it is estimated that approximately 1% of the population is affected by celiac disease, although it is frequently undiagnosed. The only way to treat this disorder is to follow a strict gluten-free diet, which involves the avoidance of all gluten-containing products, including food, beverages, and other items.
Symptoms of Celiac Disease
The symptoms associated with celiac disease can differ considerably, and not every individual who has the disorder will experience the same symptoms. Some of the most frequently observed symptoms include:
- bloating and gas,
- abdominal pain,
- diarrhea or constipation,
- fatigue, headaches,
- joint pain,
- skin rashes,
- anemia,
- malabsorption of nutrients.
- In children, celiac disease may also impede growth and development.
It is worth noting that some individuals with celiac disease may experience no symptoms or only mild and occasional symptoms.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Celiac Disease
If you believe that you may have celiac disease, it is important to seek out the advice of a healthcare professional to receive the appropriate diagnosis and management of the disorder. Diagnosis usually involves a combination of blood tests and a biopsy of the small intestine.
The only treatment available for celiac disease is a strict gluten-free diet, which requires the exclusion of all sources of gluten in food, beverages, and other products. This can be challenging, as gluten can be found in a range of unexpected places, such as medications and cosmetics.

For many people with celiac disease, adhering to a gluten-free diet can lead to significant improvements in their symptoms and long-term health outcomes. Nevertheless, it is essential to work with a healthcare professional and a registered dietitian to ensure that you are receiving all of the nutrients you need and avoiding any concealed sources of gluten. In certain cases, supplementary interventions such as vitamin and mineral supplementation or medications may be necessary to manage symptoms.
The matter at hand concerns the identification and elucidation of several health conditions that are associated with gluten, a protein composite found in certain grains. The widely known celiac disease is not the only condition with gluten-related implications. Thus, it is in our interest to take a closer look at some of these other health conditions and their potential symptoms. It is paramount to consult with a licensed healthcare professional to receive an appropriate diagnosis and subsequent treatment if a gluten-related health condition is suspected.
What are some other health conditions associated with gluten?
One such condition is non-celiac gluten sensitivity, which is also referred to as gluten intolerance. This is a condition in which individuals experience symptoms akin to celiac disease following the consumption of gluten. Unlike celiac disease, however, there is no damage to the small intestine and no specific biomarkers or blood markers that can be used to identify this condition. Symptoms of this condition may include abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, fatigue, and headaches.
Wheat Allergy
Another condition that can arise from gluten consumption is a wheat allergy, which is an immune response to the proteins found in wheat. Symptoms of this condition may include hives, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing, and anaphylaxis in severe cases. It is essential to note that wheat allergy is distinct from gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
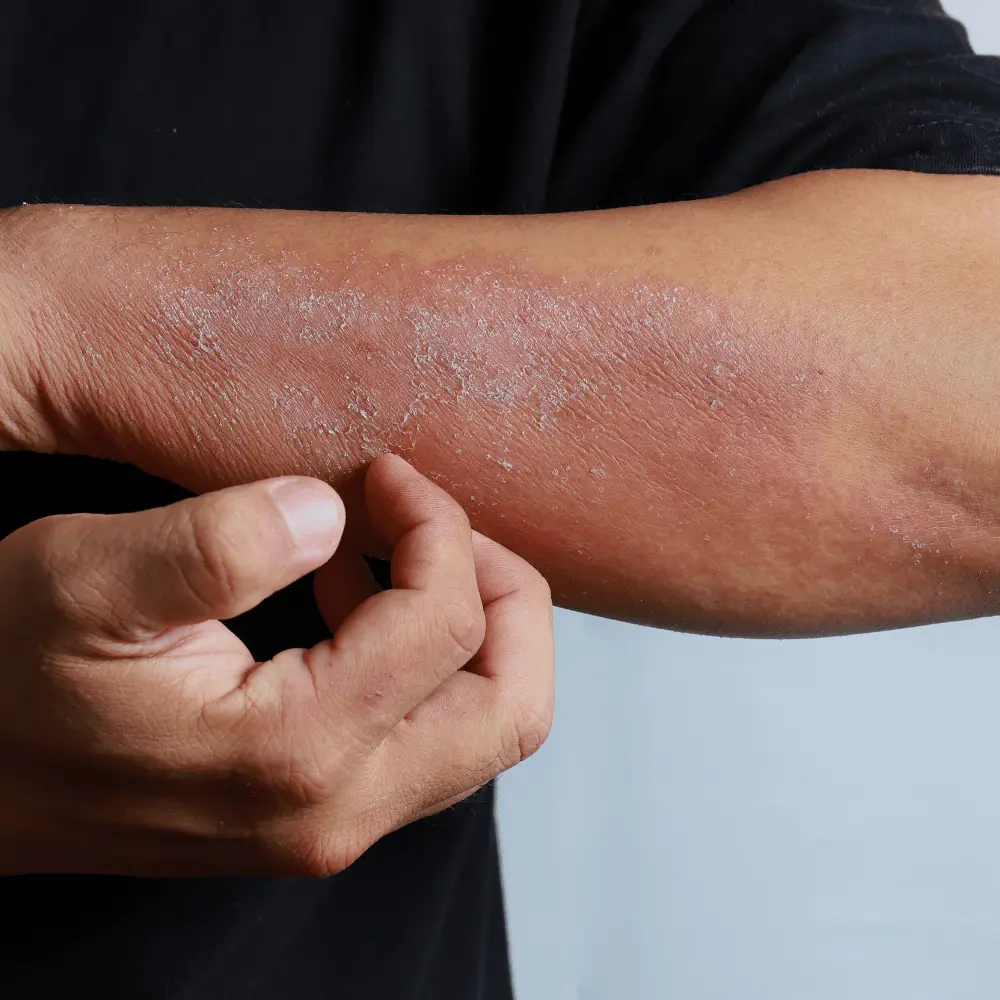
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Finally, dermatitis herpetiformis is a chronic skin condition that is characterized by itchy blisters and rashes, which can occur due to gluten sensitivity. It is related to celiac disease, and people with dermatitis herpetiformis may also have intestinal damage from gluten.
Is Coffee Safe for Celiac Disease Patients?
Coffee consumption is a widely practiced habit among millions of individuals all over the globe. Nevertheless, for individuals diagnosed with celiac disease, a perplexing question arises: is coffee safe for them to consume? In this section, we will delve into the subject of whether coffee contains gluten and its safety for celiac disease patients.
Can Coffee Contain Gluten?

One positive piece of news for coffee enthusiasts is that coffee itself is free of gluten. Coffee beans are the seed of a fruit and do not contain any gluten. Nonetheless, there exist potential sources of gluten contamination that one should be aware of.
Is Instant Coffee Gluten-Free?

The inquiry of whether instant coffee is devoid of gluten has emerged as a prevalent quandary. It’s unambiguous that instant coffee is extensively favored by many for its facile nature of preparation and expediency. Fortunately, those who adhere to a gluten-free regimen are likely to find solace in the fact that instant coffee, in general, is not laden with gluten. Nonetheless, it is paramount to exercise caution and meticulously peruse the labels of instant coffee products to avert any feasible encounter with gluten contaminants. It is further recommended to opt for certified instant coffee products that have been endorsed as gluten-free to mitigate the likelihood of inadvertent exposure to gluten.
Types of Coffee That May Contain Gluten
Although coffee beans are naturally gluten-free, particular types of coffee can contain gluten. For example, flavored coffee can contain gluten in the form of added flavorings or other additives. Moreover, some coffee houses and cafes may use syrups or toppings that contain gluten, while some instant coffees and coffee substitutes may also contain gluten.
It is imperative to be vigilant and carefully read the labels of coffee products and opt for those that are certified gluten-free to prevent any potential risks.
Cross-Contamination Risks
Another potential risk that celiac disease patients should be wary of is cross-contamination during the coffee-making process. When equipment that has been used for gluten-containing products is also used to prepare coffee, there is a risk of cross-contamination.
This can occur, for instance, if the same grinder is used for both regular and flavored coffee or if the same frothing wand is utilized for regular and flavored milk. To decrease the possibility of cross-contamination, it is crucial to inquire about the preparation process and ensure that equipment is thoroughly cleaned before use.
In conclusion, although coffee itself is gluten-free, there exist some potential sources of gluten contamination that one should be cognizant of. For celiac disease patients, it is recommended to read labels with caution, choose certified gluten-free coffee products, and inquire about the preparation process to minimize the risk of cross-contamination. By adhering to these precautions, coffee can continue to be a safe and pleasurable beverage for those with celiac disease.
Studies on the Safety of Coffee for Celiac Disease Patients

The examination of the safety of coffee consumption for individuals with celiac disease has been a topic of interest, despite the gluten-free nature of coffee. Numerous studies have sought to evaluate the compatibility of coffee with the needs of celiac disease patients. In this segment, we shall delve into the conclusions derived from these studies and the expert opinions regarding this matter.
Research Findings
Research discoveries have highlighted the possible role of coffee in triggering an immune response in individuals diagnosed with celiac disease. One study, which was documented in the Gastroenterology journal, postulated that coffee did not elicit an immune response in individuals diagnosed with celiac disease who had been adhering to a gluten-free diet for at least one year. Another study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry claimed that coffee had undetectable gluten levels.
While these findings suggest that coffee is safe for celiac disease patients to consume, there is a need for more comprehensive research to establish the correlation between coffee and celiac disease.
Expert Opinions
Expert opinions have varied on this matter. Many experts believe that coffee is safe for individuals diagnosed with celiac disease to consume, provided they take the necessary precautions to prevent any potential exposure to gluten contamination. The Celiac Disease Foundation has emphasized that coffee is naturally gluten-free, but they also advise celiac disease patients to be cautious with flavored coffee and to seek out coffee products that have been certified gluten-free. (1)
Similarly, the National Celiac Association has stated that coffee is safe for celiac disease patients, although it does caution that the coffee-making process could result in cross-contamination. To reduce the risk of cross-contamination, the organization recommends inquiring about the preparation process and opting for coffee products that have been certified gluten-free. (2)
In summary, while there is still a need for additional research to comprehend the relationship between coffee and celiac disease fully, current findings suggest that coffee is safe for individuals diagnosed with celiac disease to consume. Experts recommend that celiac disease patients take the necessary precautions to prevent any potential exposure to gluten contamination and to select coffee products that have been certified gluten-free.
Conclusion
When one considers the matter holistically, it can be concluded that coffee, generally, is typically perceived as being devoid of gluten, and those without afflictions related to gluten may partake of it without undue concern for their well-being. That being said, those who are diagnosed with celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, wheat allergy, or dermatitis herpetiformis ought to exercise great caution regarding their coffee intake and should instead opt for coffee that is guaranteed to be gluten-free.
By acquainting oneself with the nature of gluten and its impact on the human organism, individuals can make learned and wise decisions concerning their coffee choices and thereby enjoy this widely popular drink without endangering their physical health. Just as with any dietary quandary, it is highly recommended that one seeks counsel from a qualified healthcare professional to ensure that one’s dietary habits are both secure and wholesome, taking into account the individual’s singular needs and requirements.
FAQS
What are the most commendable gluten-free coffee brands?
Some of the most highly regarded gluten-free coffee brands encompass Kicking Horse Coffee, Bulletproof Coffee, Mount Hagen Coffee, and Folgers Coffee. It is essential to search for coffee products that have received certification for their gluten-free status and to meticulously scrutinize labels to sidestep any conceivable sources of gluten contamination.
Is decaf coffee exempt from gluten?
Decaffeinated coffee should be gluten-free, given that it is crafted from coffee beans that have been certified as gluten-free and do not comprise any additional ingredients that may be laced with gluten. Nevertheless, akin to regular coffee, there is a risk of cross-contamination during the coffee-making process if equipment that has been used for gluten-containing products is not properly cleansed.
Does the inclusion of milk or cream in coffee guarantee its gluten-free nature?
Milk and cream, in and of themselves, do not contain gluten and, therefore, should be permissible for individuals following a gluten-free diet. Nonetheless, it is crucial to opt for milk and cream products that have received certification for their gluten-free status, as some brands may incorporate additives or flavorings that may comprise gluten. In addition, there is a possibility of cross-contamination if the equipment that has been used for gluten-containing products is not adequately sanitized.
How can I ascertain that my coffee is free of gluten?
To ensure that your coffee is devoid of gluten, it is vital to choose coffee products that have been certified as gluten-free and meticulously inspect labels to avoid any potential sources of gluten contamination. Additionally, it is possible to inquire about the preparation process when ordering coffee to ensure that the equipment has been properly cleansed and that there is no possibility of cross-contamination. Preparing your coffee at home, utilizing ingredients and equipment that have received certification for their gluten-free status, is also a superlative technique for guaranteeing that your coffee is safe for consumption.












